Calcium Chloride Reaction With Water
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Calcium chloride | |
| Other names Neutral calcium chloride; calcium(II) chloride, calcium dichloride, E509 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| DrugBank |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.115 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E509 (acerbity regulators, ...) |
| PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| InChI
| |
| SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemic formula | Ca Cl two |
| Molar mass | 110.98 g·mol−one |
| Advent | White hygroscopic powder |
| Smell | Odorless |
| Density |
|
| Melting point | 772–775 °C (1,422–one,427 °F; 1,045–one,048 Yard) anhydrous[5] 260 °C (500 °F; 533 Thou) monohydrate, decomposes 175 °C (347 °F; 448 K) dihydrate, decomposes 45.5 °C (113.9 °F; 318.vi K) tetrahydrate, decomposes[5] 30 °C (86 °F; 303 K) hexahydrate, decomposes[1] |
| Humid point | one,935 °C (3,515 °F; 2,208 Yard) anhydrous[i] |
| Solubility in water | Anhydrous: 74.5 g/100 mL (20 °C)[2] Hexahydrate: 49.iv g/100 mL (−25 °C) 59.5 g/100 mL (0 °C) 65 g/100 mL (10 °C) 81.1 g/100 mL (25 °C)[ane] 102.two g/100 mL (xxx.two °C) α-Tetrahydrate: 90.8 g/100 mL (twenty °C) 114.4 yard/100 mL (forty °C) Dihydrate: 134.five thousand/100 mL (60 °C) 152.four grand/100 mL (100 °C)[three] |
| Solubility |
|
| Solubility in ethanol |
|
| Solubility in methanol |
|
| Solubility in acetone | 0.one g/kg (twenty °C)[4] |
| Solubility in pyridine | 16.6 1000/kg[4] |
| Acidity (pChiliad a) |
|
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | −5.47·10−v cm3/mol[i] |
| Refractive index (n D) | ane.52 |
| Viscosity |
|
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure |
|
| Space group |
|
| Indicate group |
|
| Lattice constant | a = six.259 Å, b = 6.444 Å, c = iv.17 Å (anhydrous, 17 °C)[6] α = 90°, β = 90°, γ = 90° |
| Coordination geometry | Octahedral at Caii+ centres (anhydrous) |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Heat capacity (C) |
|
| Std molar | 108.iv J/(mol·K)[ane] [v] |
| Std enthalpy of |
|
| Gibbs free energy (Δf G ⦵) | −748.81 kJ/mol[1] [5] |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | A12AA07 (WHO) B05XA07 (WHO), G04BA03 (WHO) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Primary hazards | Irritant |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  [7] [7] |
| Signal give-and-take | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H319 [7] |
| Precautionary statements | P305+P351+P338 [vii] |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | [9] ii 0 1 |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) | one,000-one,400 mg/kg (rats, oral)[eight] |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions |
|
| Other cations |
|
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Calcium chloride is an inorganic compound, a salt with the chemical formula CaClii . It is a white crystalline solid at room temperature, and information technology is highly soluble in h2o. Information technology can exist created past neutralising hydrochloric acid with calcium hydroxide.
Calcium chloride is commonly encountered every bit a hydrated solid with generic formula CaCl2·nH2O, where n = 0, i, 2, 4, and vi. These compounds are mainly used for de-icing and dust command. Because the anhydrous salt is hydroscopic and deliquescent, it is used every bit a desiccant.[ten]
Uses [edit]
De-icing and freezing-point depression [edit]

Bulk
CaCl2 for de-icing in Japan
By depressing the freezing point of water, calcium chloride is used to prevent ice formation and is used to de-ice. This awarding consumes the greatest amount of calcium chloride. Calcium chloride is relatively harmless to plants and soil. As a deicing agent, it is much more effective at lower temperatures than sodium chloride. When distributed for this use, it usually takes the course of small, white spheres a few millimeters in diameter, called prills. Solutions of calcium chloride can prevent freezing at temperatures as low as −52 °C (−62 °F), making it platonic for filling agricultural implement tires every bit a liquid ballast, aiding traction in cold climates.[11]
It is also used in domestic and industrial chemic air dehumidifiers.[12]
Road surfacing [edit]

Calcium chloride was sprayed on this route to preclude weathering, giving information technology a wet appearance fifty-fifty in dry weather.
The second largest application of calcium chloride exploits its hygroscopic nature and the tackiness of its hydrates; calcium chloride is highly hygroscopic and its hydration is an exothermic process. A concentrated solution keeps a liquid layer on the surface of dirt roads, which suppresses the formation of dust. It keeps the effectively dust particles on the road, providing a cushioning layer. If these are allowed to accident away, the large aggregate begins to shift around and the road breaks down. Using calcium chloride reduces the demand for grading by every bit much equally 50% and the need for make full-in materials as much equally lxxx%.[thirteen]
Food [edit]
The average intake of calcium chloride as food additives has been estimated to be 160–345 mg/day.[14] Calcium chloride is permitted as a food condiment in the European Marriage for apply equally a sequestrant and firming agent with the E number E509. It is considered as generally recognized as condom (GRAS) by the U.South. Nutrient and Drug Administration.[xv] Its utilise in organic crop production is more often than not prohibited under the U.s. National Organic Program.[sixteen]
In marine aquariums, calcium chloride is one way to introduce bioavailable calcium for calcium carbonate-shelled animals such equally mollusks and some cnidarians. Calcium hydroxide (limewater) or a calcium reactor can besides exist used.
Equally a firming agent, calcium chloride is used in canned vegetables, in firming soybean curds into tofu and in producing a caviar substitute from vegetable or fruit juices.[17] It is commonly used every bit an electrolyte in sports drinks and other beverages, including bottled water. The extremely salty sense of taste of calcium chloride is used to flavor pickles without increasing the nutrient'south sodium content. Calcium chloride'southward freezing-point depression properties are used to tiresome the freezing of the caramel in caramel-filled chocolate confined. Also, it is oft added to sliced apples to maintain texture.
In brewing beer, calcium chloride is sometimes used to correct mineral deficiencies in the brewing water. It affects flavour and chemical reactions during the brewing process, and tin too bear upon yeast part during fermentation.
In cheesemaking, calcium chloride is sometimes added to processed (pasteurized/homogenized) milk to restore the natural residual between calcium and protein in casein. It is added before the coagulant.
Calcium chloride is used to prevent cork spot and bitter pit on apples by spraying on the tree during the late growing season.[18]
[edit]
Drying tubes are frequently packed with calcium chloride. Kelp is dried with calcium chloride for utilise in producing sodium carbonate. Anhydrous calcium chloride has been approved by the FDA equally a packaging help to ensure dryness (CPG 7117.02).[xix]
The hydrated salt tin can be dried for re-use only will dissolve in its own h2o of hydration if heated quickly and form a hard amalgamated solid when cooled.
Other applications [edit]
Calcium chloride is used in concrete mixes to advance the initial setting, but chloride ions lead to corrosion of steel rebar, and then information technology should not be used in reinforced physical.[20] The anhydrous form of calcium chloride may also exist used for this purpose and can provide a mensurate of the moisture in physical.[21]
Calcium chloride is included as an additive in plastics and in fire extinguishers, in blast furnaces as an additive to control scaffolding (clumping and adhesion of materials that forbid the furnace accuse from descending), and in textile softener as a thinner.
The exothermic dissolution of calcium chloride is used in self-heating cans and heating pads.
In the oil manufacture, calcium chloride is used to increase the density of solids-free brines. Information technology is also used to provide inhibition of swelling clays in the h2o stage of invert emulsion drilling fluids.
CaCltwo acts as flux textile, decreasing the melting indicate, in the Davy process for the industrial production of sodium metal through the electrolysis of molten NaCl.
Calcium chloride is too used in the production of activated charcoal.
Calcium chloride tin be used to precipitate fluoride ions from water as insoluble CaF2 .
Calcium chloride is also an ingredient used in ceramic slipware. It suspends clay particles so that they float within the solution, making it easier to apply in a diversity of slipcasting techniques.
Calcium chloride dihydrate (20 percent by weight) dissolved in ethanol (95 percent ABV) has been used equally a sterilant for male animals. The solution is injected into the testes of the animal. Within one calendar month, necrosis of testicular tissue results in sterilization.[22] [23]
Cocaine producers in Republic of colombia import tons of calcium chloride to recover solvents that are on the INCB Red List and are more than tightly controlled.[24]
Metal reduction flux [edit]
Similarly, CaCl2 is used every bit a flux and electrolyte in the FFC Cambridge electrolysis procedure for titanium product, where it ensures the proper exchange of calcium and oxygen ions between the electrodes.
Hazards [edit]
Although non-toxic in modest quantities when moisture, the strongly hygroscopic backdrop of the non-hydrated salt present some hazards. Calcium chloride tin human activity as an irritant past desiccating moist peel. Solid calcium chloride dissolves exothermically, and burns tin effect in the mouth and esophagus if it is ingested. Ingestion of concentrated solutions or solid products may cause gastrointestinal irritation or ulceration.[25]
Consumption of calcium chloride tin can lead to hypercalcemia.[26]
Properties [edit]

Calcium chloride dissolves in water, producing chloride and the aquo circuitous [Ca(H2O)6]two+ . In this mode, these solutions are sources of "costless" calcium and complimentary chloride ions. This description is illustrated by the fact that these solutions react with phosphate sources to requite a solid precipitate of calcium phosphate:
- iii CaCl2 + 2 PO 3− 4 → Ca3(PO4)ii + half dozen Cl−
Calcium chloride has a very high enthalpy change of solution, indicated by considerable temperature rise accompanying dissolution of the anhydrous common salt in water. This property is the basis for its largest-scale awarding.
Molten calcium chloride can be electrolysed to give calcium metal and chlorine gas:
- CaCl2 → Ca + Cl2
Preparation [edit]
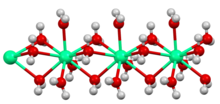
Structure of the polymeric
[Ca(H2O)6]2+ center in crystalline calcium chloride hexahydrate, illustrating the high coordination number typical for calcium complexes.
In much of the earth, calcium chloride is derived from limestone every bit a past-product of the Solvay process, which follows the net reaction beneath:[x]
- two NaCl + CaCO3 → Na2COthree + CaCl2
Northward American consumption in 2002 was 1,529,000 tonnes (3.37 billion pounds).[27]
In the The states, most of calcium chloride is obtained by purification from brine.[ commendation needed ]
As with most bulk article salt products, trace amounts of other cations from the alkali metals and alkaline earth metals (groups 1 and 2) and other anions from the halogens (grouping 17) typically occur, but the concentrations are trifling.[ citation needed ]
Occurrence [edit]
Calcium chloride occurs as the rare evaporite minerals sinjarite (dihydrate) and antarcticite (hexahydrate).[28] [29] [30] Another natural hydrate known is ghiaraite – a tetrahydrate.[31] [30] The related minerals chlorocalcite (potassium calcium chloride, KCaCliii ) and tachyhydrite (calcium magnesium chloride, CaMg2Clvi·12H2O) are also very rare.[32] [33] [30] So is true for rorisite, CaClF (calcium chloride fluoride).[34] [30]
See also [edit]
- Calcium(I) chloride
- Calcium chloride transformation
- Magnesium chloride
References [edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Lide, David R., ed. (2009). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (90th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN978-i-4200-9084-0.
- ^ "Calcium chloride (anhydrous)". ICSC. International Programme on Chemical Rubber and the European Commission.
- ^ Seidell, Atherton; Linke, William F. (1919). Solubilities of Inorganic and Organic Compounds (2nd ed.). New York: D. Van Nostrand Company. p. 196.
- ^ a b c d e f Anatolievich, Kiper Ruslan. "Properties of substance: calcium chloride". chemister.ru . Retrieved 7 July 2014.
- ^ a b c d eastward f Pradyot, Patnaik (2019). Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. p. 162. ISBN978-0-07-049439-8.
- ^ a b c d Müller, Ulrich (2006). Inorganic Structural Chemistry. wiley.com (2nd ed.). England: John Wiley & Sons Ltd. p. 33. ISBN978-0-470-01864-iv.
- ^ a b c Sigma-Aldrich Co., Calcium chloride.
- ^ Donald E. Garrett (2004). Handbook of Lithium and Natural Calcium Chloride. p. 379. ISBN978-0080472904 . Retrieved 29 August 2018.
Its toxicity upon ingestion, is indicated by the test on rats: oral LD50 (rat) is ane.0–1.4 g/kg (the lethal dose for half of the test animals, in this case rats...)
- ^ "MSDS of Calcium chloride". fishersci.ca. Fisher Scientific. Retrieved vii July 2014.
- ^ a b Robert Kemp, Suzanne E. Keegan "Calcium Chloride" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemical science 2000, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:ten.1002/14356007.a04_547
- ^ "Binary Phase diagram: The Calcium Chloride – water system". Aqueous Solutions Aps. October 2016. Archived from the original on 26 June 2019. Retrieved twenty April 2017.
- ^ "Keeping Things Dry out". humantouchofchemistry.com. Archived from the original on 26 October 2014. Retrieved 23 October 2014.
- ^ "Dust: Don't Eat Information technology! Control Information technology!". Road Direction & Engineering science Journal. United states of america Roads (TranSafety Inc.). 1 June 1998. Archived from the original on 29 October 2007. Retrieved 9 August 2006.
- ^ Calcium Chloride SIDS Initial Assessment Profile, UNEP Publications, SIAM 15, Boston, 22–25 Oct 2002, pp. 13–14.
- ^ 21 CFR § 184.1193
- ^ 7 CFR § 205.602
- ^ "Apple Caviar Technique". StarChefs Studio. StarChefs.com. Apr 2004. Retrieved 9 Baronial 2006.
- ^ "Cork Spot and Biting Pit of Apples", Richard C. Funt and Michael A. Ellis, Ohioline.osu.edu/factsheet/plpath-fru-01
- ^ "CPG 7117.02". FDA Compliance Articles. US Nutrient and Drug Assistants. March 1995. Retrieved 3 December 2007.
- ^ "Accelerating Concrete Set Time". Federal Highway Assistants. 1 June 1999. Archived from the original on 17 Jan 2007. Retrieved 16 January 2007.
- ^ National Enquiry Council (U.S.). Building Inquiry Found (1962). Adhesives in Edifice: Selection and Field Application; Pressure-sensitive Tapes. National Academy of Science-National Inquiry Council. pp. 24–5.
- ^ Koger, Nov 1977, "Calcium Chloride, Practical Necrotizing Agent", Journal of the American Association of Bovine Practitioners (USA), (Nov 1977), v. 12, p. 118–119
- ^ Jana, K.; Samanta, P.K. (2011). "Clinical evaluation of non-surgical sterilization of male cats with single intra-testicular injection of calcium chloride". BMC Vet. Res. 7: 39. doi:10.1186/1746-6148-vii-39. PMC3152893. PMID 21774835.
- ^ Smith, Michael; Simpson, Cam (26 Oct 2020). "Narcos Are Waging a New Drug State of war Over a Texas Company'southward Basic Chemical". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on 26 October 2020. Retrieved 26 Oct 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "Product Safety Cess (PSA): Calcium Chloride". Dow Chemic Company. 2 May 2006. Archived from the original on 17 September 2009. Retrieved 22 July 2008.
- ^ "Calcium Chloride Possible Side Affects". www.drugs.com.
- ^ Calcium Chloride SIDS Initial Assessment Profile, UNEP Publications, SIAM 15, Boston, 22–25 October 2002, page 11.
- ^ "Sinjarite". www.mindat.org.
- ^ "Antarcticite". www.mindat.org.
- ^ a b c d "List of Minerals". www.ima-mineralogy.org. 21 March 2011.
- ^ "Ghiaraite". www.mindat.org.
- ^ "Chlorocalcite". www.mindat.org.
- ^ "Tachyhydrite". world wide web.mindat.org.
- ^ "Rorisite". www.mindat.org.
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN978-0-08-037941-8.
External links [edit]
- International Chemical Safety Card 1184
- Production and Awarding Information (Formerly Dow Chemical Calcium Chloride division)
- Written report on steel corrosion past chloride including CaCltwo
- Collection of calcium chloride reports and articles
- Calcium chloride, Anhydrous MSDS
- Difusivity of calcium chloride
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Institutes of Occupational Prophylactic and Health, "Calcium Chloride (anhydrous)"
Calcium Chloride Reaction With Water,
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcium_chloride#:~:text=Calcium%20chloride%20dissolves%20in%20water,calcium%20and%20free%20chloride%20ions.
Posted by: nethourt1965.blogspot.com



0 Response to "Calcium Chloride Reaction With Water"
Post a Comment